Publications
2024
-
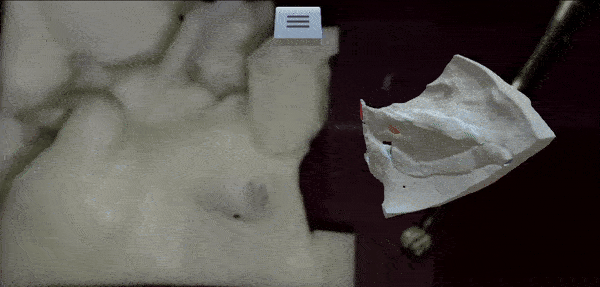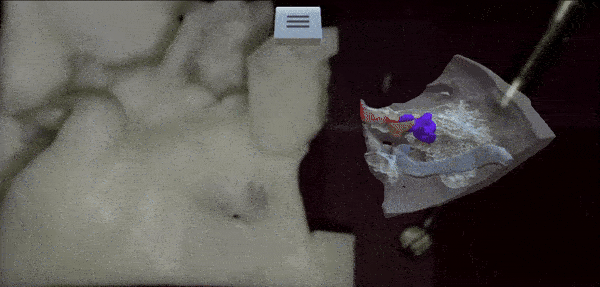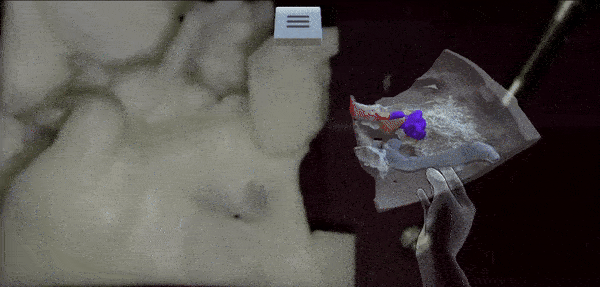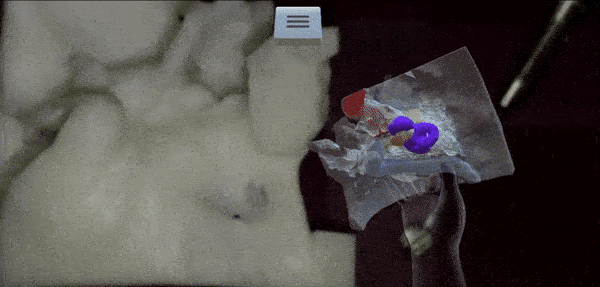 From Microscope to Head-Mounted Display: Integrating Hand Tracking into Microsurgical Augmented RealityTrishia El Chemaly, Caio Athayde Neves, Fanrui Fu, and 2 more authorsInternational Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 2024
From Microscope to Head-Mounted Display: Integrating Hand Tracking into Microsurgical Augmented RealityTrishia El Chemaly, Caio Athayde Neves, Fanrui Fu, and 2 more authorsInternational Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 2024
2023
-
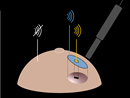 Hearing Tumors: Interactive Shape Sonification for Breast Cancer LocalizationTrishia El Chemaly*, Laura Schutz*, Emmanuelle Weber, and 4 more authorsACM Special Interest Group on Computer-Human Interaction (SIGCHI), (accepted), 2023
Hearing Tumors: Interactive Shape Sonification for Breast Cancer LocalizationTrishia El Chemaly*, Laura Schutz*, Emmanuelle Weber, and 4 more authorsACM Special Interest Group on Computer-Human Interaction (SIGCHI), (accepted), 2023About 20 percent of patients undergoing breast-conserving surgery require reoperation due to cancerous tissue remaining inside the breast. Breast cancer localization systems utilize auditory feedback to convey the distance between a localization probe and a small marker (seed) implanted into the breast tumor prior to surgery. However, no information on the location of the tumor margin is provided. To reduce the reoperation rate by improving the usability and accuracy of the surgical task, we developed an auditory display using shape sonification to assist with tumor margin localization. Accuracy and usability of the interactive shape sonification were determined on models of the female breast in three user studies with both breast surgeons and non-clinical participants. The comparative studies showed a significant increase in usability (p<0.05) and localization accuracy (p<0.001) of the shape sonification over the auditory feedback currently used in surgery.
-
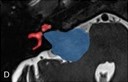 Automated Radiomic Analysis of Vestibular Schwannomas and Inner Ears Using Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted and T2-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Sequences and Artificial IntelligenceCaio A Neves, George S Liu, Trishia El Chemaly, and 3 more authorsOtology & Neurotology, 2023
Automated Radiomic Analysis of Vestibular Schwannomas and Inner Ears Using Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted and T2-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Sequences and Artificial IntelligenceCaio A Neves, George S Liu, Trishia El Chemaly, and 3 more authorsOtology & Neurotology, 2023Objective To objectively evaluate vestibular schwannomas (VSs) and their spatial relationships with the ipsilateral inner ear (IE) in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) using deep learning. Study Design Cross-sectional study. Patients A total of 490 adults with VS, high-resolution MRI scans, and no previous neurotologic surgery. Interventions MRI studies of VS patients were split into training (390 patients) and test (100 patients) sets. A three-dimensional convolutional neural network model was trained to segment VS and IE structures using contrast-enhanced T1-weighted and T2-weighted sequences, respectively. Manual segmentations were used as ground truths. Model performance was evaluated on the test set and on an external set of 100 VS patients from a public data set (Vestibular-Schwannoma-SEG). Main Outcome Measure(s) Dice score, relative volume error, average symmetric surface distance, 95th-percentile Hausdorff distance, and centroid locations. Results Dice scores for VS and IE volume segmentations were 0.91 and 0.90, respectively. On the public data set, the model segmented VS tumors with a Dice score of 0.89 ± 0.06 (mean ± standard deviation), relative volume error of 9.8 ± 9.6%, average symmetric surface distance of 0.31 ± 0.22 mm, and 95th-percentile Hausdorff distance of 1.26 ± 0.76 mm. Predicted VS segmentations overlapped with ground truth segmentations in all test subjects. Mean errors of predicted VS volume, VS centroid location, and IE centroid location were 0.05 cm3, 0.52 mm, and 0.85 mm, respectively. Conclusions A deep learning system can segment VS and IE structures in high-resolution MRI scans with excellent accuracy. This technology offers promise to improve the clinical workflow for assessing VS radiomics and enhance the management of VS patients.
-
 Stereoscopic calibration for augmented reality visualization in microscopic surgeryTrishia El Chemaly, Caio Athayde Neves, Christoph Leuze, and 2 more authorsInternational Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 2023
Stereoscopic calibration for augmented reality visualization in microscopic surgeryTrishia El Chemaly, Caio Athayde Neves, Christoph Leuze, and 2 more authorsInternational Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 2023Purpose Middle and inner ear procedures target hearing loss, infections, and tumors of the temporal bone and lateral skull base. Despite the advances in surgical techniques, these procedures remain challenging due to limited haptic and visual feedback. Augmented reality (AR) may improve operative safety by allowing the 3D visualization of anatomical structures from preoperative computed tomography (CT) scans on real intraoperative microscope video feed. The purpose of this work was to develop a real-time CT-augmented stereo microscope system using camera calibration and electromagnetic (EM) tracking. Methods A 3D printed and electromagnetically tracked calibration board was used to compute the intrinsic and extrinsic parameters of the surgical stereo microscope. These parameters were used to establish a transformation between the EM tracker coordinate system and the stereo microscope image space such that any tracked 3D point can be projected onto the left and right images of the microscope video stream. This allowed the augmentation of the microscope feed of a 3D printed temporal bone with its corresponding CT-derived virtual model. Finally, the calibration board was also used for evaluating the accuracy of the calibration. Results We evaluated the accuracy of the system by calculating the registration error (RE) in 2D and 3D in a microsurgical laboratory setting. Our calibration workflow achieved a RE of 0.11 ± 0.06 mm in 2D and 0.98 ± 0.13 mm in 3D. In addition, we overlaid a 3D CT model on the microscope feed of a 3D resin printed model of a segmented temporal bone. The system exhibited small latency and good registration accuracy. Conclusion We present the calibration of an electromagnetically tracked surgical stereo microscope for augmented reality visualization. The calibration method achieved accuracy within a range suitable for otologic procedures. The AR process introduces enhanced visualization of the surgical field while allowing depth perception.
-
 The user experience design of a novel microscope within SurgiSim, a virtual reality surgical simulatorMadeleine Lotbiniere-Bassett, Arthur Volpato Batista, Carolyn Lai, and 4 more authorsInternational Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 2023
The user experience design of a novel microscope within SurgiSim, a virtual reality surgical simulatorMadeleine Lotbiniere-Bassett, Arthur Volpato Batista, Carolyn Lai, and 4 more authorsInternational Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 2023Purpose Virtual reality (VR) simulation has the potential to advance surgical education, procedural planning, and intraoperative guidance. “SurgiSim” is a VR platform developed for the rehearsal of complex procedures using patient-specific anatomy, high-fidelity stereoscopic graphics, and haptic feedback. SurgiSim is the first VR simulator to include a virtual operating room microscope. We describe the process of designing and refining the VR microscope user experience (UX) and user interaction (UI) to optimize surgical rehearsal and education. Methods Human-centered VR design principles were applied in the design of the SurgiSim microscope to optimize the user’s sense of presence. Throughout the UX’s development, the team of developers met regularly with surgeons to gather end-user feedback. Supplemental testing was performed on four participants. Results Through observation and participant feedback, we made iterative design upgrades to the SurgiSim platform. We identified the following key characteristics of the VR microscope UI: overall appearance, hand controller interface, and microscope movement. Conclusion Our design process identified challenges arising from the disparity between VR and physical environments that pertain to microscope education and deployment. These roadblocks were addressed using creative solutions. Future studies will investigate the efficacy of VR surgical microscope training on real-world microscope skills as assessed by validated performance metrics.
2019
-
 Towards Point-of-Care Heart Failure Diagnostic Platforms: BNP and NT-proBNP BiosensorsTrishia El Chemaly*, Hussein Alawieh*, Samir Alam, and 1 more authorSensors, 2019
Towards Point-of-Care Heart Failure Diagnostic Platforms: BNP and NT-proBNP BiosensorsTrishia El Chemaly*, Hussein Alawieh*, Samir Alam, and 1 more authorSensors, 2019Heart failure is a class of cardiovascular diseases that remains the number one cause of death worldwide with a substantial economic burden of around $18 billion incurred by the healthcare sector in 2017 due to heart failure hospitalization and disease management. Although several laboratory tests have been used for early detection of heart failure, these traditional diagnostic methods still fail to effectively guide clinical decisions, prognosis, and therapy in a timely and cost-effective manner. Recent advances in the design and development of biosensors coupled with the discovery of new clinically relevant cardiac biomarkers are paving the way for breakthroughs in heart failure management. Natriuretic neurohormone peptides, B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal prohormone of BNP (NT-proBNP), are among the most promising biomarkers for clinical use. Remarkably, they result in an increased diagnostic accuracy of around 80% owing to the strong correlation between their circulating concentrations and different heart failure events. The latter has encouraged research towards developing and optimizing BNP biosensors for rapid and highly sensitive detection in the scope of point-of-care testing. This review sheds light on the advances in BNP and NT-proBNP sensing technologies for point-of-care (POC) applications and highlights the challenges of potential integration of these technologies in the clinic. Optical and electrochemical immunosensors are currently used for BNP sensing. The performance metrics of these biosensors—expressed in terms of sensitivity, selectivity, reproducibility, and other criteria—are compared to those of traditional diagnostic techniques, and the clinical applicability of these biosensors is assessed for their potential integration in point-of-care diagnostic platforms.
2018
-
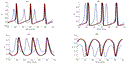 Towards A Biomechanical Model for Ultrasound Effect on Neural ExcitabilityRima El Hassan, Trishia El Chemaly, and Massoud KhraicheIn 2018 IEEE International Multidisciplinary Conference on Engineering Technology (IMCET), 2018
Towards A Biomechanical Model for Ultrasound Effect on Neural ExcitabilityRima El Hassan, Trishia El Chemaly, and Massoud KhraicheIn 2018 IEEE International Multidisciplinary Conference on Engineering Technology (IMCET), 2018Ultrasound has emerged as a promising non-invasive approach for neural modulation. This presents a challenge for understanding the mechanisms and pathways involved in modulating neural function via mechanical perturbations. In this work, we present a model that incorporates the biomechanics of a single neuron and its impact on membrane potential. We incorporate membrane tension, ion channels and ion specific transmembrane proteins, and the flexoelectric effect of the neural membrane. We attempt to show the impact of ultrasound stimulation on a single neuron taking into consideration intensity and frequency and finally discuss how our data compares to past studies.
2017
-
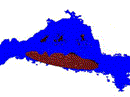 MRI and stereo vision surface reconstruction and fusionTrishia El Chemaly, Françoise J. Siepel, Sandy Rihana, and 3 more authorsIn 2017 Fourth International Conference on Advances in Biomedical Engineering (ICABME), 2017
MRI and stereo vision surface reconstruction and fusionTrishia El Chemaly, Françoise J. Siepel, Sandy Rihana, and 3 more authorsIn 2017 Fourth International Conference on Advances in Biomedical Engineering (ICABME), 2017Breast cancer, the most commonly diagnosed cancer in women worldwide, is mostly detected through a biopsy where tissue is extracted and chemically examined or pathologist assessed. Medical imaging plays a valuable role in targeting malignant tissue accurately and guiding the radiologist during needle insertion in a biopsy. This paper proposes a computer software that can process and combine 3D reconstructed surfaces from different imaging modalities, particularly Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and camera, showing a visualization of important features and investigates its feasibility. The development of this software aims to combine the detectability of MRI with the physical space of the camera. It demonstrates that the registration accuracy of the proposed system is acceptable and has potential for clinical application.